Blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most disruptive innovations of the 21st century. It is reshaping industries, enhancing transparency, and revolutionizing how data is stored and transferred. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a secure and immutable manner. As we dive deeper into this article, you will discover the immense potential and practical applications of blockchain in various sectors.
The growing interest in blockchain stems from its ability to provide trust and security without the need for intermediaries. Unlike traditional systems, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, ensuring that every transaction is verified and recorded transparently. This technology is not limited to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin but extends to areas such as supply chain management, healthcare, and finance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of blockchain, its advantages, challenges, and real-world applications. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a business professional, or simply curious about this groundbreaking technology, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need to understand its significance and impact.
Read also:Is Louis Litt Gay Exploring The Characters Sexual Orientation And Beyond
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Blockchain
- How Blockchain Works
- Types of Blockchain
- Advantages of Blockchain
- Challenges of Blockchain
- Real-World Applications
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
- Blockchain in Supply Chain
- Future of Blockchain
- Conclusion
Introduction to Blockchain
Blockchain technology was initially introduced as the backbone of Bitcoin, the world's first decentralized cryptocurrency. However, its potential goes far beyond digital currencies. A blockchain is essentially a distributed ledger that records transactions in blocks, which are then linked together in chronological order. This creates an unalterable chain of data that is transparent and secure.
One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional databases, where data is stored in a single location, blockchain operates on a network of nodes. Each node has a copy of the entire ledger, ensuring that no single entity has control over the system. This decentralization enhances security and reduces the risk of fraud or tampering.
What Makes Blockchain Unique?
Blockchain stands out due to its ability to provide trust in a trustless environment. Here are some of the unique characteristics of blockchain:
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Transparency: All participants in the network can view the transactions, ensuring accountability.
- Security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Decentralization: The absence of a central authority makes the system resilient to attacks and failures.
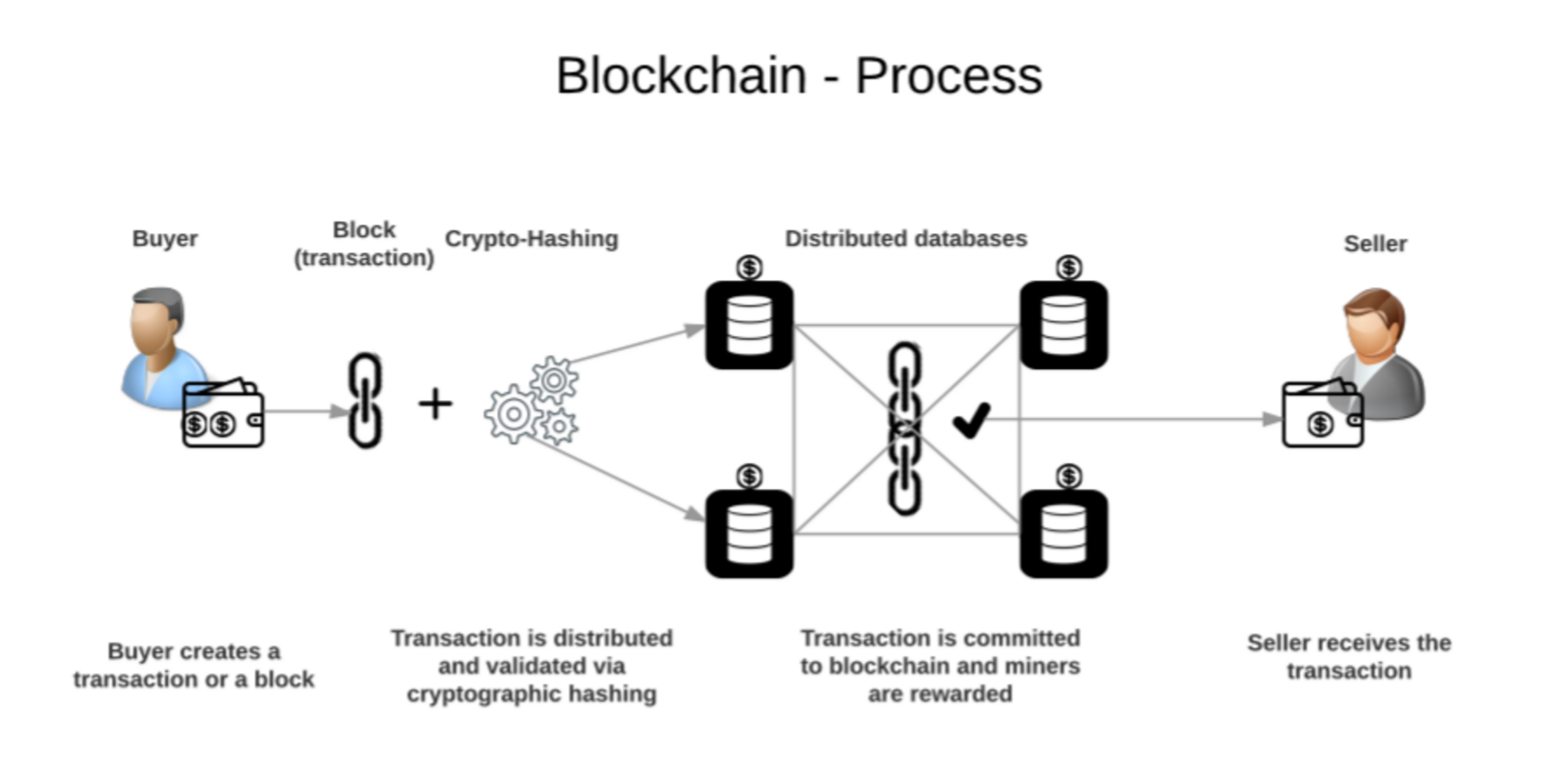
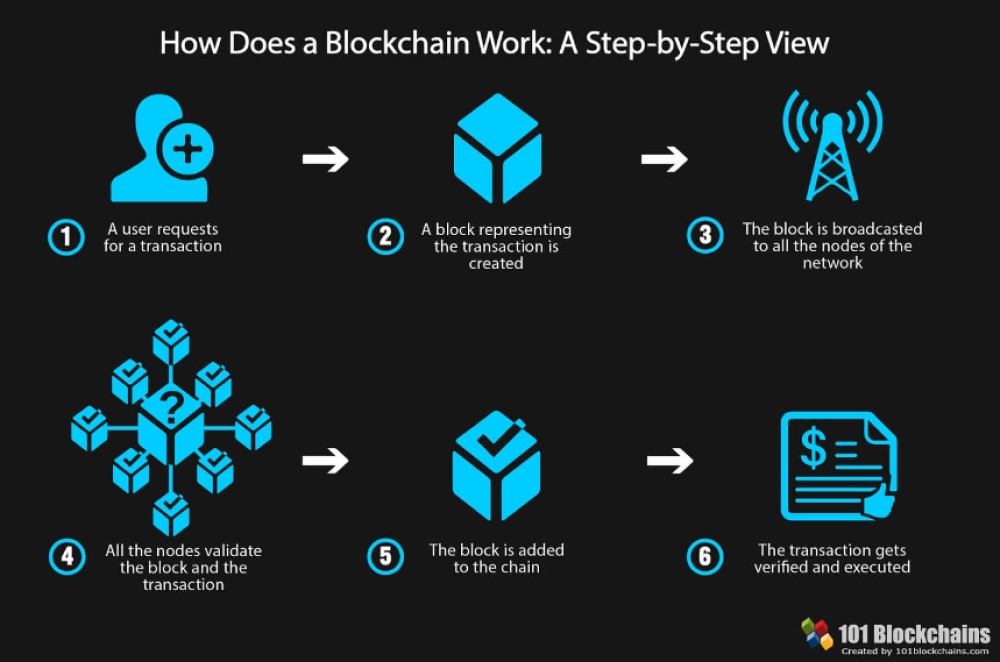
How Blockchain Works
To understand the inner workings of blockchain, it's essential to break down its key components. At its core, blockchain operates on three fundamental principles: blocks, nodes, and miners.
Blocks
Blocks are the building blocks of a blockchain. Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a unique cryptographic hash. Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be changed or deleted.
Nodes
Nodes are the computers that form the blockchain network. They play a crucial role in validating and propagating transactions across the network. Every node has a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring that the system remains decentralized and secure.
Read also:Pat Lalama Unveiling The Extraordinary Journey And Achievements
Miners
Miners are responsible for adding new blocks to the blockchain. They solve complex mathematical puzzles to verify transactions and earn rewards in the form of cryptocurrency. This process, known as proof-of-work, ensures the integrity of the blockchain.
Types of Blockchain
Not all blockchains are created equal. Depending on their purpose and design, blockchains can be classified into three main types: public, private, and consortium.
Public Blockchain
Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to anyone. They allow anyone to participate in the network, making them highly decentralized and transparent. However, this openness comes at the cost of scalability and privacy.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are restricted to a specific group of participants. They offer greater control and privacy but sacrifice some level of decentralization. Private blockchains are commonly used in enterprise settings where confidentiality is paramount.
Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains strike a balance between public and private blockchains. They are governed by a group of organizations, ensuring that no single entity has control over the network. This makes them ideal for collaborative projects involving multiple stakeholders.
Advantages of Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive solution for various industries. Some of the key benefits include:
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain's cryptographic protocols and decentralized architecture make it highly secure and resistant to attacks.
- Increased Transparency: All participants in the network can view the transactions, fostering trust and accountability.
- Cost Efficiency: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain reduces operational costs and improves efficiency.
- Traceability: Blockchain provides a permanent and immutable record of transactions, enabling easy tracking and verification.
Challenges of Blockchain
Despite its many advantages, blockchain technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. These challenges include:
- Scalability: Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum struggle to handle a large number of transactions, leading to slow processing times and high fees.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The lack of clear regulations surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies creates uncertainty for businesses and investors.
- Energy Consumption: Proof-of-work consensus mechanisms used by some blockchains consume significant amounts of energy, raising environmental concerns.
Real-World Applications
Blockchain technology is already being used in various industries to solve real-world problems. Here are some of the most promising applications:
Finance
In the financial sector, blockchain is being used to streamline cross-border payments, reduce transaction costs, and enhance security. Companies like Ripple and Stellar are leading the charge in this area.
Supply Chain
Blockchain is transforming supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility and traceability. Companies like Walmart and Maersk are leveraging blockchain to improve efficiency and reduce fraud.
Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain is being used to securely store and share patient data, ensuring privacy and interoperability. This technology can also help combat counterfeit drugs by tracking the entire supply chain.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are perhaps the most well-known application of blockchain technology. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital currencies rely on blockchain to ensure secure and transparent transactions. While cryptocurrencies have gained popularity, they also face challenges such as volatility and regulatory scrutiny.
How Cryptocurrencies Work
Cryptocurrencies use blockchain to create a decentralized digital currency that is not controlled by any government or financial institution. Transactions are verified by miners and recorded on the blockchain, ensuring security and transparency.
Blockchain in Supply Chain
Supply chain management is one of the most promising areas for blockchain adoption. By providing a transparent and immutable record of transactions, blockchain can help reduce fraud, improve efficiency, and enhance customer trust.
Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chain
- Improved Traceability: Blockchain enables end-to-end tracking of products, ensuring authenticity and quality.
- Increased Efficiency: By automating processes and reducing paperwork, blockchain can streamline supply chain operations.
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain's cryptographic protocols ensure the integrity and confidentiality of supply chain data.
Future of Blockchain
The future of blockchain looks promising, with ongoing research and development in areas such as scalability, interoperability, and privacy. As the technology matures, we can expect to see more innovative applications and wider adoption across industries.
Emerging trends such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and blockchain-based identity systems are pushing the boundaries of what blockchain can achieve. These innovations have the potential to reshape industries and create new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we store, transfer, and manage data. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature makes it an attractive solution for various industries. From finance and supply chain to healthcare and beyond, blockchain is already making a significant impact.
We encourage you to explore the possibilities of blockchain further and consider how it can benefit your business or personal endeavors. Don't forget to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. For more informative articles and updates on emerging technologies, be sure to check out our other content on the website. Together, let's embrace the future of blockchain and unlock its full potential.