RemoteIoT has emerged as a revolutionary technology that is reshaping industries worldwide. With the increasing demand for remote monitoring and control systems, businesses are now leveraging RemoteIoT to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve decision-making processes. This cutting-edge technology allows organizations to gather real-time data, automate operations, and streamline workflows seamlessly.
As industries evolve, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) with remote capabilities is becoming essential. RemoteIoT offers businesses the ability to manage assets, monitor equipment, and analyze data from anywhere in the world. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of RemoteIoT, its applications, benefits, and implementation strategies to help you harness its full potential.
Whether you're a business owner, IT professional, or tech enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to implement RemoteIoT effectively. From understanding the basics to exploring advanced applications, we will cover everything you need to know about this transformative technology.
Read also:Exploring The Depths Of Creative Automation Undressing Ai
Table of Contents
- Introduction to RemoteIoT
- Key Benefits of RemoteIoT
- Applications of RemoteIoT
- RemoteIoT Architecture
- Security Considerations in RemoteIoT
- Implementing RemoteIoT Solutions
- Common Challenges in RemoteIoT
- Emerging Trends in RemoteIoT
- Case Studies of RemoteIoT
- The Future of RemoteIoT
Introduction to RemoteIoT
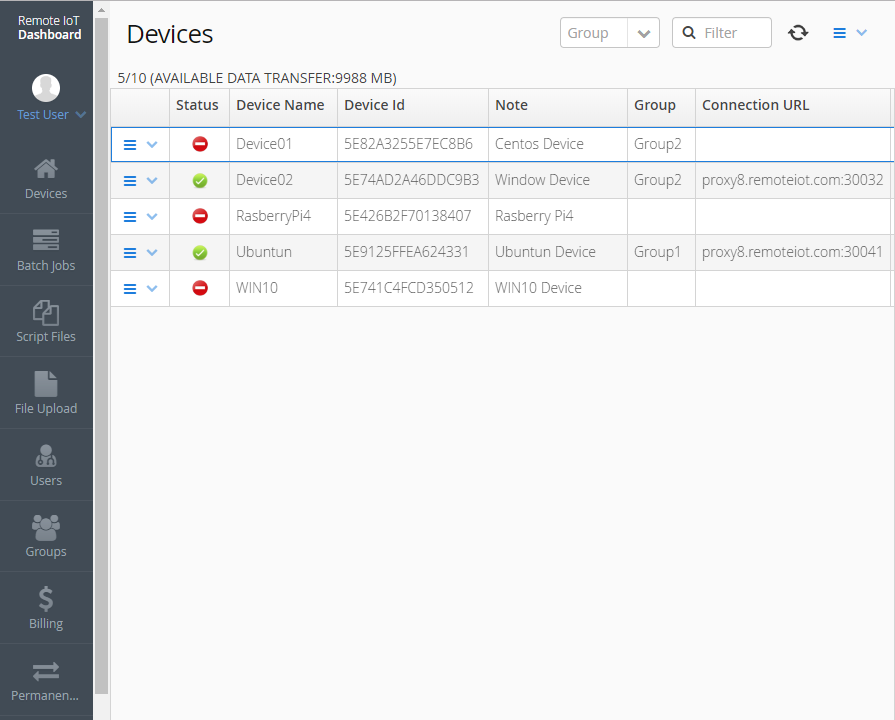
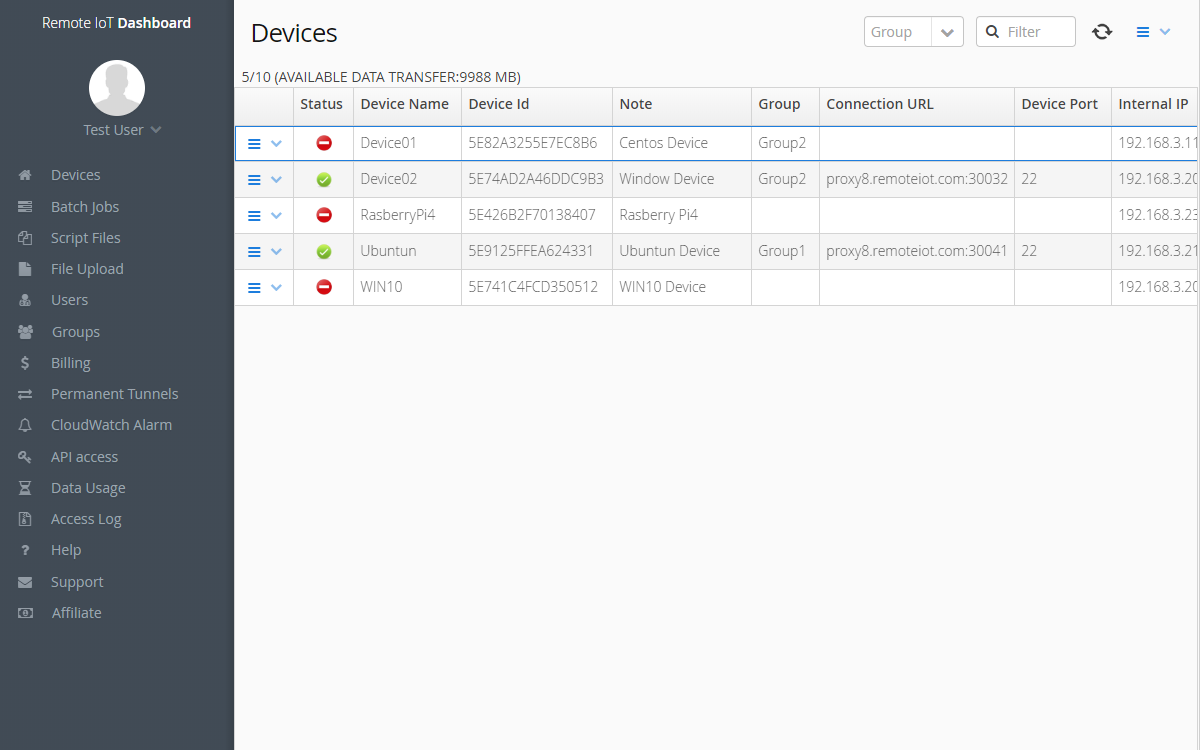
RemoteIoT refers to the integration of IoT devices and systems with remote access capabilities. This technology enables users to monitor, control, and manage connected devices from distant locations. The concept of RemoteIoT combines hardware, software, and network infrastructure to create a robust ecosystem for data collection, analysis, and automation.
The rise of RemoteIoT can be attributed to advancements in wireless communication, cloud computing, and sensor technology. These innovations have made it possible to deploy scalable and cost-effective solutions for various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and transportation.
How RemoteIoT Works
At its core, RemoteIoT operates through a network of interconnected devices that communicate with each other and a central server. Data collected by sensors and devices is transmitted to the cloud, where it is processed and analyzed. Users can access this information through web-based dashboards or mobile applications, enabling them to make informed decisions.
- Data collection through sensors and devices
- Transmission of data via wireless communication protocols
- Processing and analysis in the cloud
- Remote access through user interfaces
Key Benefits of RemoteIoT
Implementing RemoteIoT can bring numerous advantages to businesses and organizations. These benefits span across operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Operational Efficiency
RemoteIoT allows businesses to automate repetitive tasks, reducing the need for manual intervention. This leads to improved productivity and streamlined workflows, as employees can focus on more critical tasks.
Cost Savings
By enabling remote monitoring and maintenance, RemoteIoT helps organizations reduce travel costs and minimize downtime. Predictive maintenance capabilities further contribute to cost savings by preventing equipment failures.
Read also:Al Weaver Unveiling The Remarkable Journey Of A True Visionary
Enhanced Decision-Making
With access to real-time data, businesses can make data-driven decisions that are more accurate and timely. This leads to better resource allocation, improved customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.
Applications of RemoteIoT
RemoteIoT has a wide range of applications across various industries. From smart cities to industrial automation, this technology is transforming the way businesses operate and deliver value to their customers.
Smart Agriculture
In agriculture, RemoteIoT is used for monitoring soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health. Farmers can optimize irrigation systems, reduce water wastage, and increase crop yields by leveraging real-time data.
Healthcare
RemoteIoT plays a crucial role in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. Wearable devices and sensors enable healthcare providers to track vital signs, detect anomalies, and deliver timely interventions, improving patient outcomes.
Industrial Automation
Manufacturing plants use RemoteIoT for monitoring production lines, predicting equipment failures, and optimizing energy consumption. This results in increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved product quality.
RemoteIoT Architecture
A typical RemoteIoT architecture consists of several components, including sensors, gateways, cloud platforms, and user interfaces. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring seamless communication and data flow within the system.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors are responsible for collecting data from the physical environment, while actuators enable remote control of devices. These components form the foundation of any RemoteIoT system, providing the necessary inputs and outputs for operation.
Gateways and Connectivity
Gateways act as intermediaries between sensors and the cloud, facilitating data transmission and protocol conversion. Connectivity options such as Wi-Fi, cellular, and satellite ensure reliable communication even in remote locations.
Cloud Platforms
Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure for data storage, processing, and analysis. They enable scalable and flexible solutions that can accommodate growing demands and evolving requirements.
Security Considerations in RemoteIoT
As RemoteIoT systems become more prevalent, security concerns have become a significant challenge. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of communication networks are critical to maintaining trust and reliability.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is essential for safeguarding information transmitted between devices and the cloud. Advanced encryption protocols, such as AES and TLS, help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Authentication and Authorization
Implementing robust authentication and authorization mechanisms ensures that only authorized users can access and control RemoteIoT systems. Multi-factor authentication and role-based access control are effective strategies for enhancing security.
Regular Updates and Patching
Keeping software and firmware up to date is crucial for addressing vulnerabilities and protecting against emerging threats. Regular updates and patching help maintain the security and reliability of RemoteIoT systems.
Implementing RemoteIoT Solutions
Successfully implementing RemoteIoT solutions requires careful planning and execution. Organizations must consider various factors, including infrastructure requirements, budget constraints, and technical expertise.
Assessing Requirements
Before deploying RemoteIoT, businesses should conduct a thorough assessment of their needs and objectives. This includes identifying key performance indicators, defining success metrics, and evaluating potential risks.
Selecting the Right Technology
Choosing the appropriate technology stack is critical for ensuring compatibility and scalability. Organizations should consider factors such as hardware specifications, software capabilities, and integration options when selecting RemoteIoT solutions.
Training and Support
Providing adequate training and support to employees is essential for maximizing the benefits of RemoteIoT. This includes offering workshops, documentation, and technical assistance to ensure smooth adoption and operation.
Common Challenges in RemoteIoT
Despite its numerous advantages, RemoteIoT presents several challenges that organizations must address to achieve successful implementation. These challenges include technical limitations, regulatory compliance, and user adoption.
Interoperability Issues
Different devices and systems may use incompatible protocols and standards, making it difficult to achieve seamless integration. Organizations should prioritize interoperability when selecting RemoteIoT solutions to avoid potential conflicts.
Regulatory Compliance
RemoteIoT systems must comply with various regulations and standards, such as GDPR and HIPAA, depending on the industry and region. Ensuring compliance requires thorough understanding and adherence to legal requirements.
User Adoption
Encouraging user adoption can be challenging, especially when introducing new technologies. Organizations should focus on user experience and provide adequate training to overcome resistance and promote acceptance.
Emerging Trends in RemoteIoT
The RemoteIoT landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Several trends are shaping the future of this industry, offering exciting opportunities for innovation and growth.
Edge Computing
Edge computing enables data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. This trend is gaining traction in RemoteIoT as organizations seek to enhance real-time capabilities and reduce reliance on cloud infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence
Integrating AI with RemoteIoT allows for advanced analytics and automation, enabling predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and optimized decision-making. AI-driven solutions are becoming increasingly popular in various applications, from smart homes to industrial automation.
Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming a key focus for RemoteIoT solutions, with organizations prioritizing energy efficiency and environmental impact. Green IoT initiatives aim to reduce carbon footprints and promote sustainable practices across industries.
Case Studies of RemoteIoT
Real-world examples of RemoteIoT implementations demonstrate the technology's potential to drive innovation and deliver value. These case studies highlight successful deployments and the impact they have had on businesses and communities.
Smart City Initiative
A city in Europe implemented RemoteIoT to monitor traffic patterns, optimize public transportation, and reduce congestion. The project resulted in improved traffic flow, reduced emissions, and enhanced quality of life for residents.
Remote Patient Monitoring
A healthcare provider adopted RemoteIoT for monitoring patients with chronic conditions. The system enabled continuous tracking of vital signs, early detection of health issues, and timely interventions, leading to better patient outcomes.
Industrial Predictive Maintenance
An automotive manufacturer deployed RemoteIoT for predictive maintenance of production equipment. The solution reduced downtime by 30% and lowered maintenance costs by 25%, significantly improving operational efficiency.
The Future of RemoteIoT
The future of RemoteIoT looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and expanding applications across industries. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, RemoteIoT will play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of connected systems.
In the coming years, we can expect to see increased adoption of RemoteIoT in emerging markets, driven by growing demand for smart solutions and sustainable practices. Collaboration between stakeholders, including governments, academia, and industry leaders, will be crucial for driving innovation and addressing challenges in this rapidly evolving field.
Conclusion
RemoteIoT has proven to be a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize industries and improve lives. By understanding its applications, benefits, and implementation strategies, businesses can harness its power to achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and innovation. As the technology continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be key to unlocking its full potential.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with RemoteIoT in the comments section below. Feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into emerging technologies and trends. Together, let's build a smarter, more connected future!